| |
HVAC System
 HVAC System
HVAC System
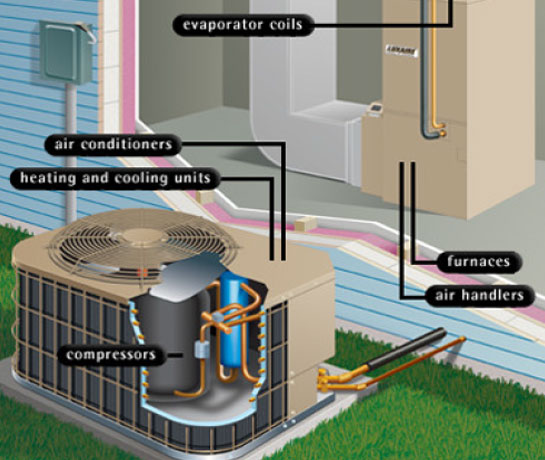 What is HVAC???
What is HVAC???
H = HEATING
V = VENTILATION
A = AIR
C = CONDITIONING
VARIOUS APPLICATIONS OF HVAC
-
Shopping Malls
-
Auditorium & Theatres
-
Hospitals
-
Hotels and Restaurant
-
Offices
-
Commercial Complex
-
Luxury Apartments
-
InfoTech Parks
-
Pharma Industry
-
Telecom Industry
-
And many more……..!!!!!!
OUR HVAC SYSTEM!!!!!
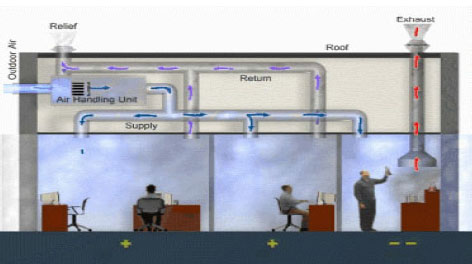
Mainly our company consists of 2 different types of HVAC
systems:-
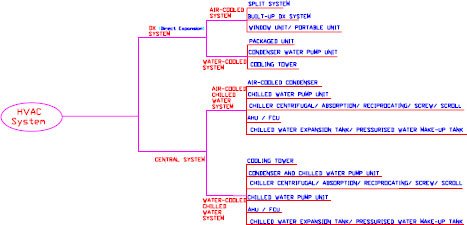
FLOW DIAGRAM SHOWING VARIOUS TYPES OF HVAC Systems
Schematic diagram with Description of each Component in
HVAC plant
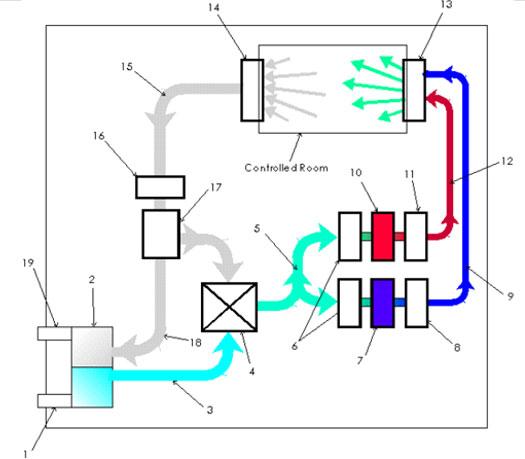
External fresh air inlet. Heat
Exchange Unit: Exhaust air to be released in the
atmosphere is used to normalize the
temperature of the incoming fresh air. Both air flows are
maintained separated. Fresh air
intake conduit: Supplies fresh air to the
distributor.
Distributor: Electronically controlled, it manages
the air flowing into the cooling and heating units and the
ratio of fresh to recycled air. Air supply
ducts: Supply air to the heating and cooling units. Electrostatic filters: Remove the
smallest particles of dust, smoke, pollens and other
contaminants. Cooling
(A/C) Unit: Electronically controlled, cools down the
intake air to a temperature as a function of demand and
other environment variables. - Cold air fan: Variable
speed turbine type fan that maintains certain (positive)
pressure in the cold air column.
Cold air
column: Delivers cold air throughout the building. Heating
(Furnace) Unit: Electronically controlled, heats up
the intake air to a temperature as a function of demand and
other environment variables. Warm air
fan: Variable speed turbine type fan that maintains
certain (positive) pressure in the warm air column. Warm air
column: Delivers warm air throughout the building. Fresh air
inlet: Electronically controlled, it allows a mixture
of cold and warm air from the respective columns in the
room. Exhaust air
outlets: Electronically controlled, remove exhaust
air from the room. Exhaust air
column: Delivers the exhaust air from the building
back to the power plant to complete the cycle. Exhaust air
fan: Variable speed turbine type fan that maintains
certain (negative) pressure in the exhaust air column. Recycled
air distributor: Electronically controlled, it
manages the volume of exhaust air released in the atmosphere
and the portion of it used for recycling. Exhaust air
conduit: Air to be released is forced into the Heat
Exchange Unit, where it is used to normalize the temperature
of the incoming fresh air. External
exhaust air outlet.
Description:-
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) is the
technology of indoor and automotive environmental comfort.
HVAC is important in the design of medium to large
industrial and officebuildings such as skyscrapers and in
marine environments such as aquariums, where safe and
healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to
temperature and humidity, using fresh air from outdoors.
Heating:- There are many different types of heating
systems. Central heating is often used in cool climates to
heat houses and public buildings. Such a system contains a
boiler, furnace, or heat pump to warm
water, steam, or air in a central location such as a furnace
room in a home or a mechanical room in
a large building. The use of water as the heat transfer
medium is known as hydronics. These systems also contain either duct. Ducts are used in heating,
ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) to deliver and remove air. These needed airflows
include, for example, supply air, return
air, and exhaust air. Ducts also deliver, most commonly as
part of the supply air, ventilation air.
Work for forced air systems or piping to distribute a heated
fluid to radiators to transfer this heat to
the air. The term radiator in this context is misleading
since most heat transfer from the heat
exchanger is by convection, not radiation. The radiators may
be mounted on walls or installed
within the floor to give floor heat.
Ventilation:- An air handling unit is used for the
heating and cooling of air in a central location.
Ventilation is the process of changing or replacing air in
any space to control temperature or
remove any combination of moisture, odors, smoke, heat,
dust, airborne bacteria, or carbon dioxide,
and to replenish oxygen. Ventilation includes both the
exchange of air with the outside as well as
circulation of air within the building. It is one of the
most important factors for maintaining
acceptable indoor air quality in buildings.
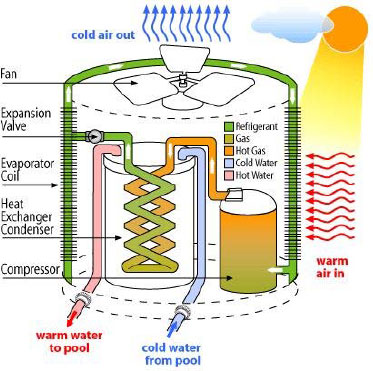
Air conditioning :- Air conditioning and refrigeration
are provided through the removal of heat. Heat can be removed
through radiation, convection, and by heat pump systems
through the refrigeration cycle.
Refrigeration conduction media such as water, air, ice, and
chemicals are referred to as refrigerants. An air conditioning
system provides cooling, ventilation, and humidity control for
all or part of a building. The refrigeration cycle uses four
essential elements to cool. The system refrigerant starts its
cycle in a gaseous state.
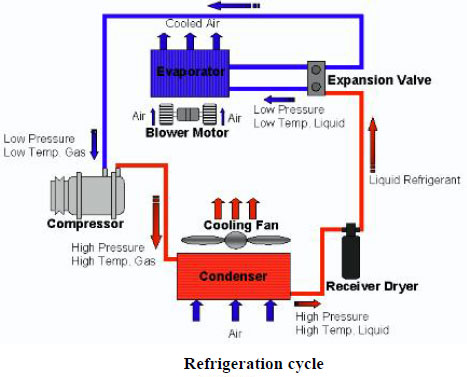
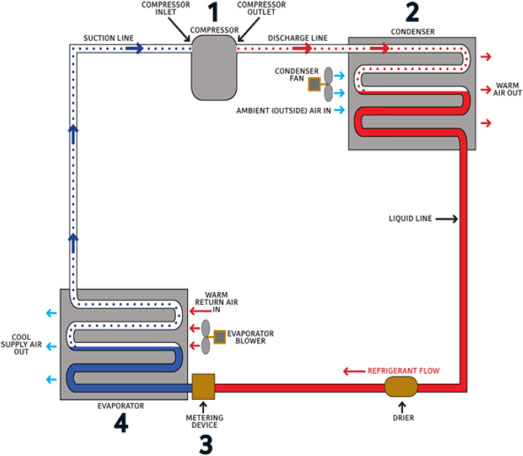
The compressor pumps the refrigerant
gas up to a high pressure and temperature. From there it
enters a heat exchanger (sometimes called a "condensing coil"
or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outside,
cools, and condenses into its liquid phase.The liquid
refrigerant is returned to another heat exchanger where it is
allowed to evaporate; hence the heat exchanger is often called
an "evaporating coil" or evaporator. A metering device
regulates the refrigerant liquid to flow at theproper rate. As
the liquid refrigerant evaporates it absorbs energy (heat)
from the inside air, returns to the compressor, and repeats
the cycle. In the process, heat is absorbed from indoors and
transferred outdoors, resulting in cooling of the building.
BASIC OPERATION CYCLE
(HVAC)
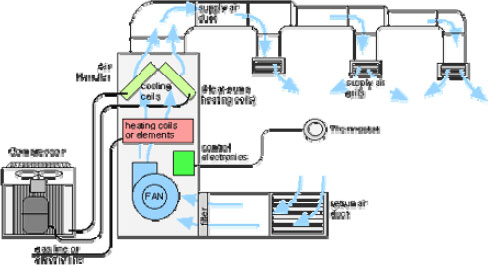
Air Handling Unit
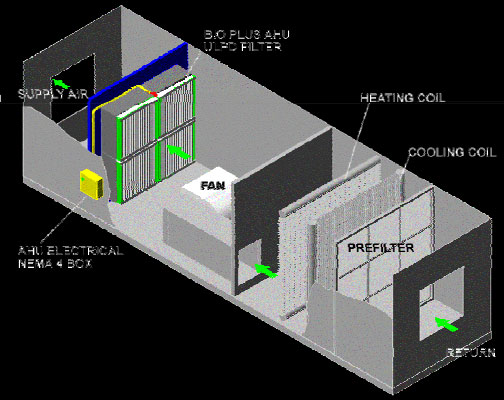
Air handling unit is a device used to
condition and circulate air as part of a heating, ventilating,
and
air-conditioning (hvac) system. An air handler is usually a
large metal box containing a blower,
heating or cooling elements, filter racks or chambers, sound
attenuators, and dampers. Air handlers usually connect to a
ductwork ventilation system that distributes the conditioned
air through the building and returns it to the ahu. Sometimes
AHU’s discharge (supply) and admit (return) air directly to
and from the space served without ductwork. Small air
handlers, for local use, are called terminal units, and may
only include an air filter, coil, and blower; these simple
terminal units are called blower coils or fan coil units. A
larger air handler that conditions 100% outside air, and no
recirculated air, is known as a makeup air unit (mau). An air
handler designed for outdoor use, typically on roofs, is known
as a packaged unit (pu) or rooftop unit (rtu). |
|